In our modern world, where the impacts of climate change are increasingly evident and environmental degradation looms large, the call for innovative solutions has never been more urgent. Fortunately, the wisdom of nature offers a myriad of answers to the challenges we face. Nature-based solutions (NbS) harness the power of ecosystems to address a wide range of issues, from mitigating climate change to enhancing biodiversity and promoting sustainable development. In this blog, we delve into various types of nature-based solutions, highlighting their significance and potential for creating a healthier, more resilient planet.
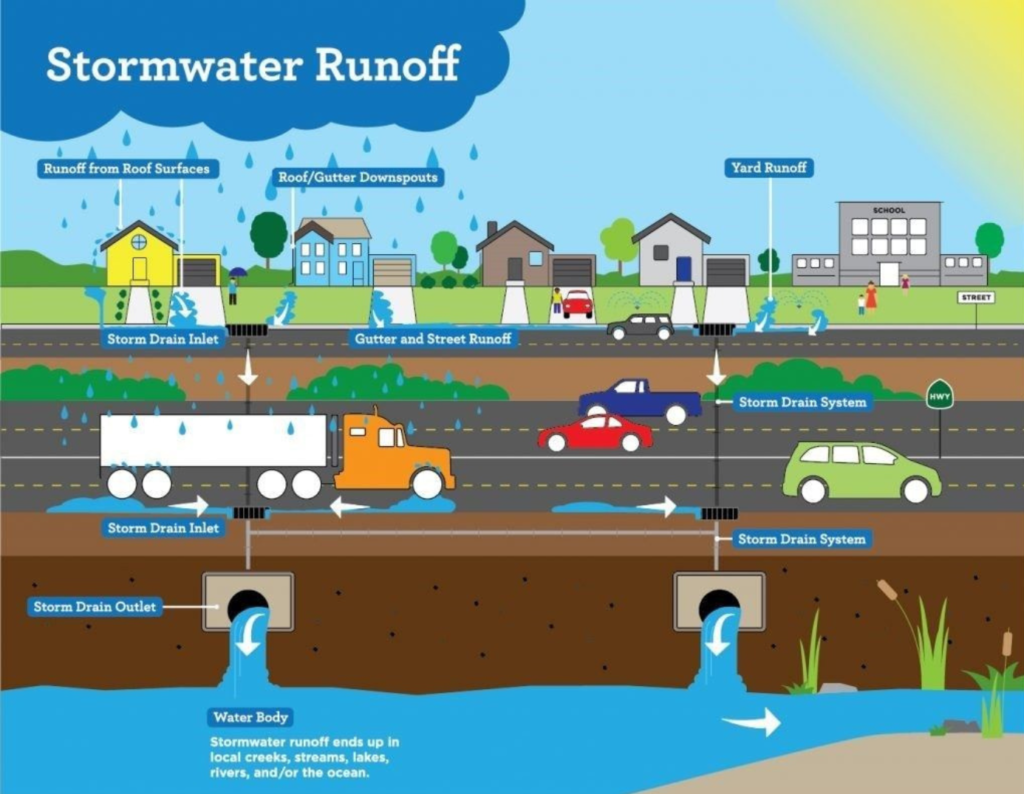
- Green Infrastructure: Imagine strolling through a city where rooftops are adorned with gardens, and streets are lined with trees and lush green spaces. This is the vision of green infrastructure—a type of NBS that mimics natural ecosystems to manage storm-water, reduce urban heat island effects, and enhance biodiversity. From green roofs to permeable pavements, green infrastructure offers cities a sustainable way to manage water and create healthier, more resilient communities. By integrating nature into urban landscapes, green infrastructure not only improves air and water quality but also provides habitat for wildlife and enhances the overall quality of life for residents.
Read more about Nature-based Solutions here
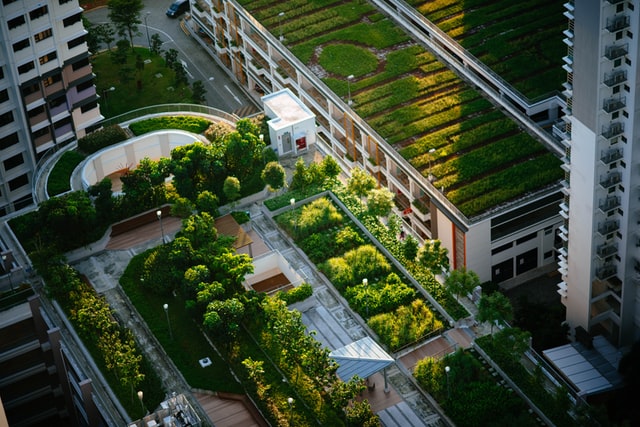

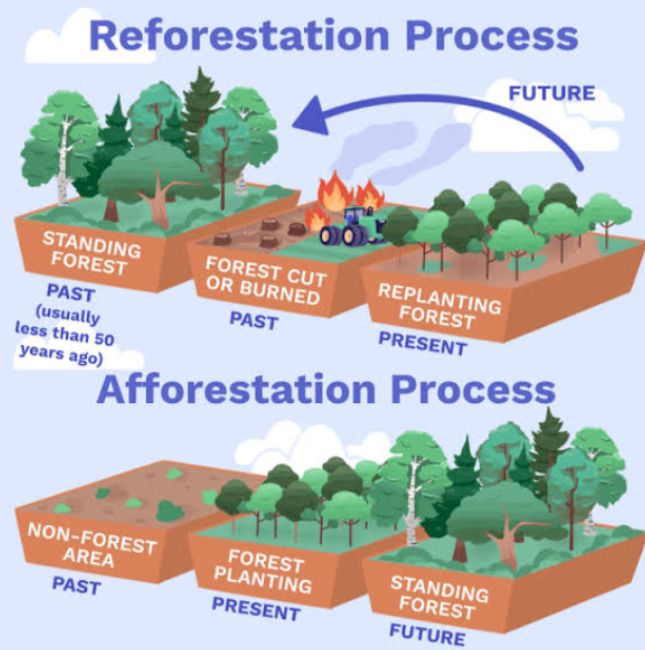
- Reforestation and Afforestation: The simple act of planting trees can have a profound impact on the environment. Reforestation and afforestation—types of NBS that involve restoring and expanding forest cover—help to sequester carbon, mitigate climate change, and restore biodiversity. Whether it’s restoring degraded landscapes or creating new forests in urban areas, tree planting initiatives are a powerful tool for combating environmental degradation and promoting sustainable land use.
- Sustainable Agriculture: In a world where food security and environmental sustainability are increasingly intertwined, sustainable agriculture emerges as a critical type of NbS. Practices such as agroforestry, organic farming, and crop rotation not only promote soil health and biodiversity but also help to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and sequestering carbon. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices, farmers can improve yields, protect natural resources, and build resilient food systems for the future.

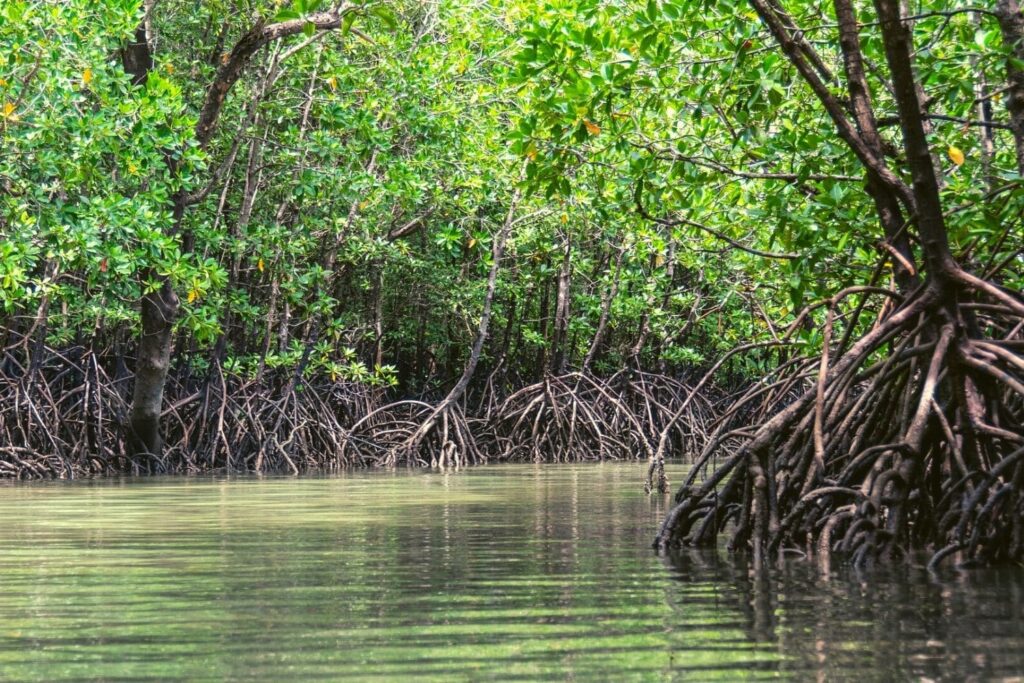
- Coastal Restoration: Coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs, provide invaluable services to both humans and the environment. Coastal restoration—a type of NbS that involves restoring and protecting these ecosystems—helps to stabilize shorelines, protect against erosion, and provide habitat for marine life. From mangrove reforestation to oyster reef restoration, coastal restoration projects play a crucial role in building resilience to climate change and safeguarding coastal communities.

- Natural Flood Management: In an era of increasing climate variability and extreme weather events, natural flood management offers a sustainable alternative to traditional flood control measures. By restoring natural floodplains, wetlands, and riparian zones, natural flood management helps to slow the flow of water, reduce flood risk, and improve water quality. From re-meandering rivers to creating floodplain forests, natural flood management techniques harness the power of nature to build resilience to flooding and protect vulnerable communities.
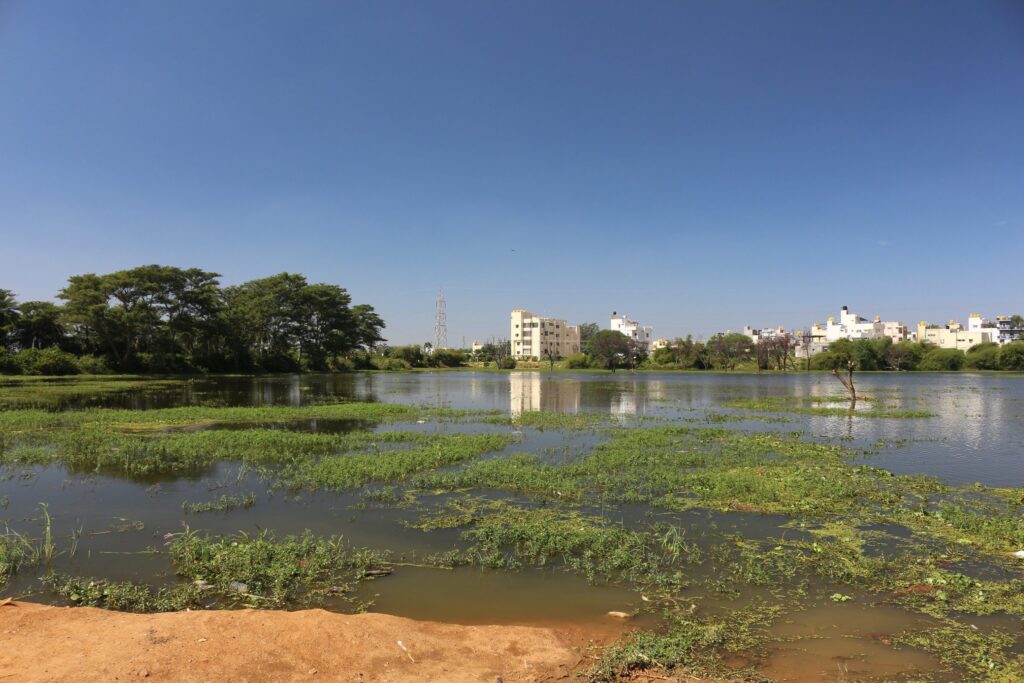
- Wetlands Protection: Wetlands ecosystems are vital parts of hydrological cycle, support rich biodiversity, sequester carbon and provide a wide range of ecosystem services such as water storage, water purification, flood mitigation, erosion control, aquifer recharge, microclimate regulation, aesthetic enhancement of landscapes while simultaneously supporting many significant recreational, social and cultural activities. Several people depend on wetlands for their livelihood as well as for food and water. Protecting wetlands is vital.

Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of the modern world, Nature-based Solutions offer a beacon of hope—a reminder that by working with nature, rather than against it, we can address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. From green infrastructure in cities to coastal restoration projects along our shores, the diverse types of NbS showcased in this blog represent a holistic and sustainable approach to building a more resilient and equitable world for all.

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team- Business development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech.
Reference:
https://www.naturebasedsolutionsinitiative.org/what-are-nature-based-solutionshttps://www.fema.gov/emergency-managers/risk-management/climate-resilience/nature-based-solutions/typeshttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772411522000015
https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rstb.2019.0120




